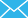
The basic principle of PSA-CO technology is to use the adsorption selectivity of the adsorbent to adsorb CO in the mixed gas, and then to desorb CO by decompression or vacuumizing to achieve the CO separation.
It can be seen from the comparison with the adsorption curve of 5A molecular sieve that the adsorption performance of the copper-loaded molecular sieve is more excellent. On one hand, it has higher adsorbing capacity of CO as a result of the complex adsorption of the active Cu+ to CO. On the other hand, almost no other gases can be adsorbed because CuCl covers the original active centers of the molecular sieve on the surface, and it also reduces the adsorption to CO2 which was highly adsorbed before. Therefore, when processing the feed gas with a low CO2 content, it is possible to directly absorb and separate CO without removing CO2, which is the so called one-stage PSA. The superior performance of Cu-based molecular sieves lies in the fact that their adsorption principle combines physical and chemical methods together, utilizing the large specific surface area of the molecular sieve carrier and the complexation between Cu+ and CO. We dispersed a single layer of CuCl on the inner surface of the molecular sieve, and finally produced highly-efficient copper-loaded molecular sieve.




 2019-12-09
2019-12-09