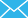
The uniformity of air distribution in the adsorption tower has a great influence on the oxygen plant performance, making the design of the air distributor critical. The uneven air distribution will inevitably lead to high airflow velocity in some parts and lower in others. In places with higher velocity, the airflow is larger and the nitrogen will go through prematurely, resulting in a "channeling" phenomenon which will affect the efficiency of the adsorbent and make it difficult to ensure the oxygen capacity and purity of the VPSA and PSA oxygen unit. In addition, where the airflow velocity is larger, the scouring effect of the airflow on the molecular sieve is intensified, which may lead to fluidization or even fragmentation of the molecular sieve. If the adsorption tower has improper air distribution design, and the designed airflow speed is too high, the problems caused by uneven air distribution will be more serious or even make VPSA and PSA oxygen generators unable to operate normally.
PKU Pioneer’s oxygen generation plants adopt radial-flow adsorption vessels where the air flows radially from outside to the inside of the adsorbers, which can ensure the uniform division and consistent flow rate when the air stream enters the adsorber tower and passes through the adsorbent bed. Meanwhile, the radial tower also has the advantages of smaller pressure drop, lower resistance, higher adsorbent utilization rate, smaller dead space, larger processing air amount, shorter cycle and easier capacity extension, which is more reasonable than the structure of axial flow adsorption tower. The capacity of a single set of two-tower VPSA oxygen unit can be doubled and the unit energy consumption of oxygen production can be reduced by at least 10%.




 2022-07-25
2022-07-25